top of page
GLIAL CONTROL OF SYNAPSE DEVELOPMENT AND INHIBITION
Ephrin-B/Eph Receptor Signaling
Eph: Video
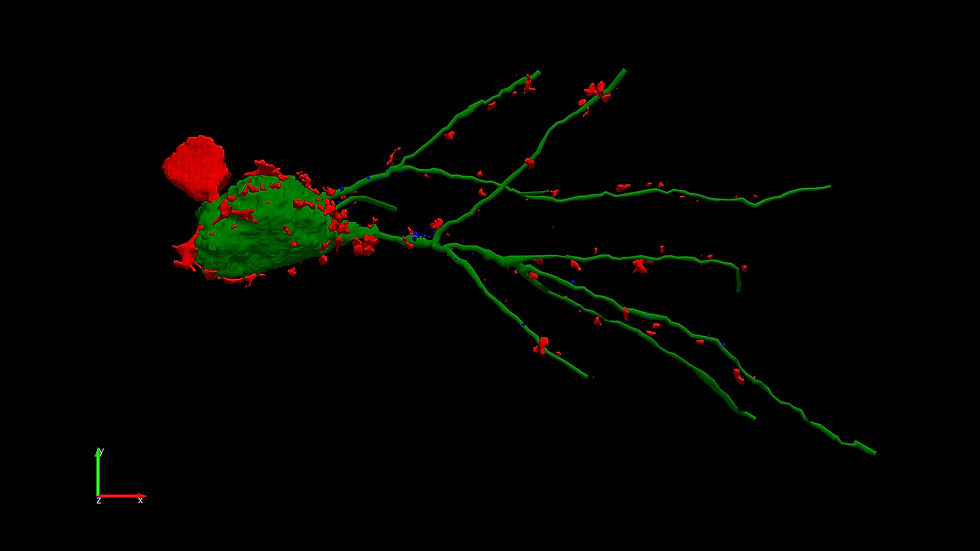
Glial control of normal synapse development and plasticity during learning; and injury-induced synapse remodeling in neurodegenerative diseases:
Our new studies suggest that ephrin-B/Eph receptor signaling is involved in astrocyte-mediated synapse development in the hippocampus (Nguyen et al., 2020), synaptic plasticity in adult brain (Koeppen et al., 2018), as well as their remodeling in TBI (Nikolakopoulou et al., 2016) and ALS (Wu et al., 2017; Baggio et al., 2021). In the ongoing studies, we propose to investigate new mechanisms of astrocyte-mediated development of inhibitory synapses in the hippocampus, in particular their role in the development of inhibitory perisomatic innervation by PV cells. These studies will provide a significant advances by unveiling a new role for ephrin-B1 in astrocytes and elucidating new mechanisms by which astrocytes regulate synapse development and plasticity. Furthermore, these findings will establish a foundation for future studies of astrocyte-mediated synaptogenesis in clinically relevant conditions as recent work linked EphB receptors to neurologic disorders. Given widespread and growing interest in the astrocyte-mediated mechanisms that regulate learning and memory, and EphB receptor role in neurodevelopmental disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, we suspect this project has potential for future clinical applications.
Eph: Research
bottom of page
